Chromatin mapping and single-cell immune profiling defines the temporal dynamics of ibrutinib drug response in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Supplementary Website
Study overview
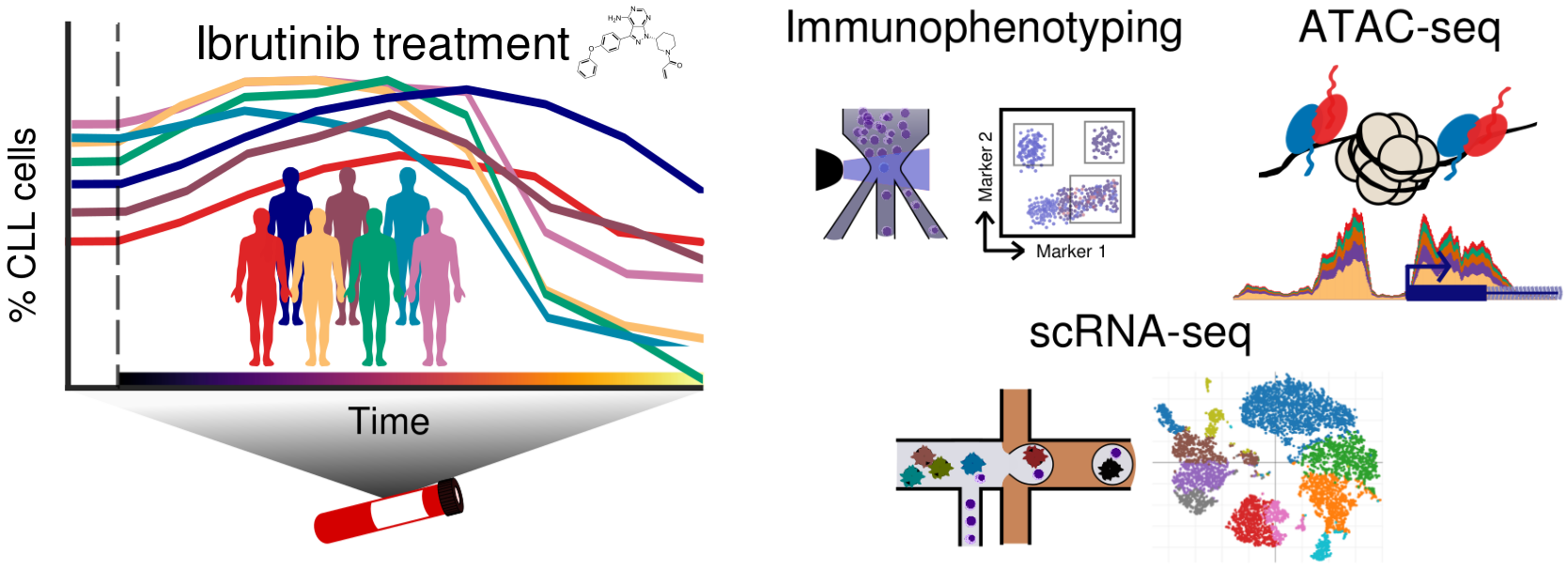
Chromatin mapping and single-cell immune profiling of ibrutinib drug response in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
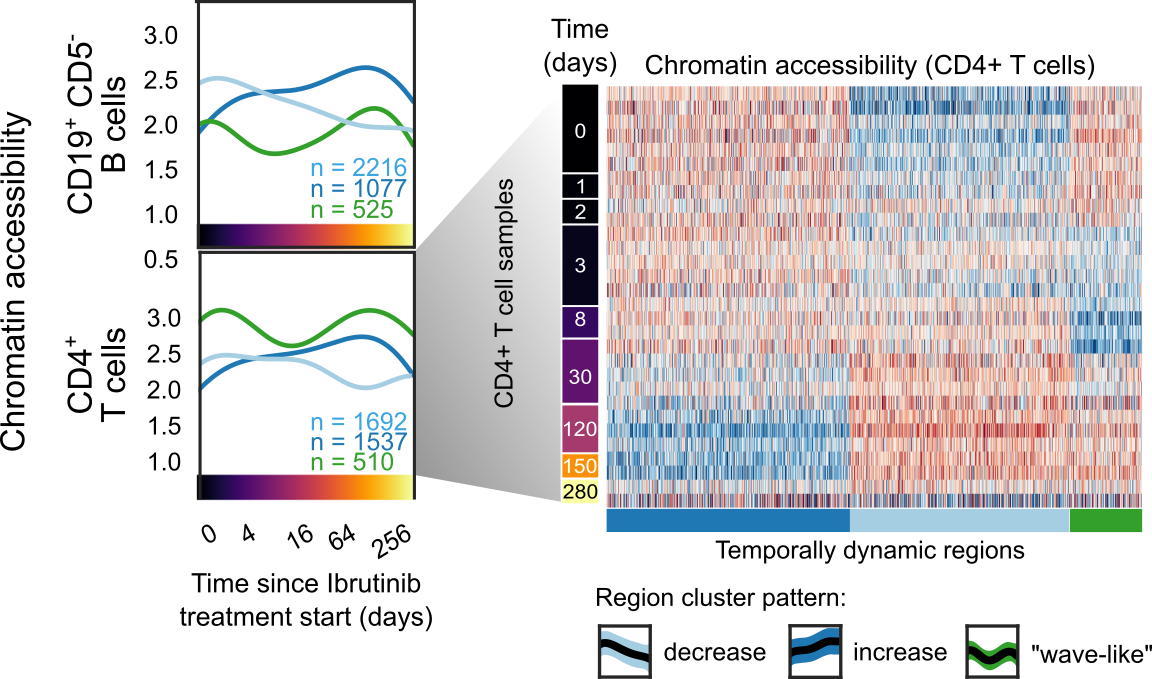
Chromatin profiling in six immune cell types identifies ibrutinib-induced regulatory changes beyond CLL cells
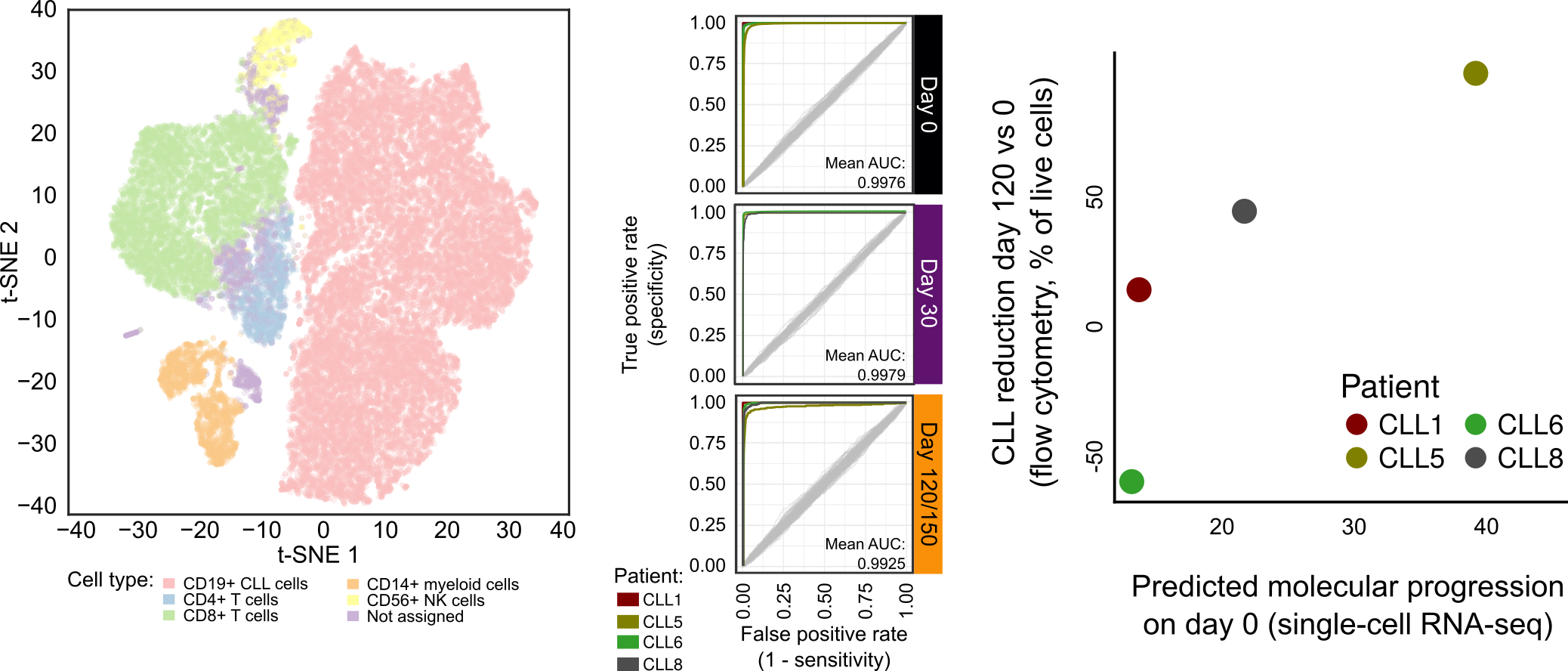
Single-cell RNA-seq uncovers patient-to-patient heterogeneity in the molecular response to ibrutinib treatment
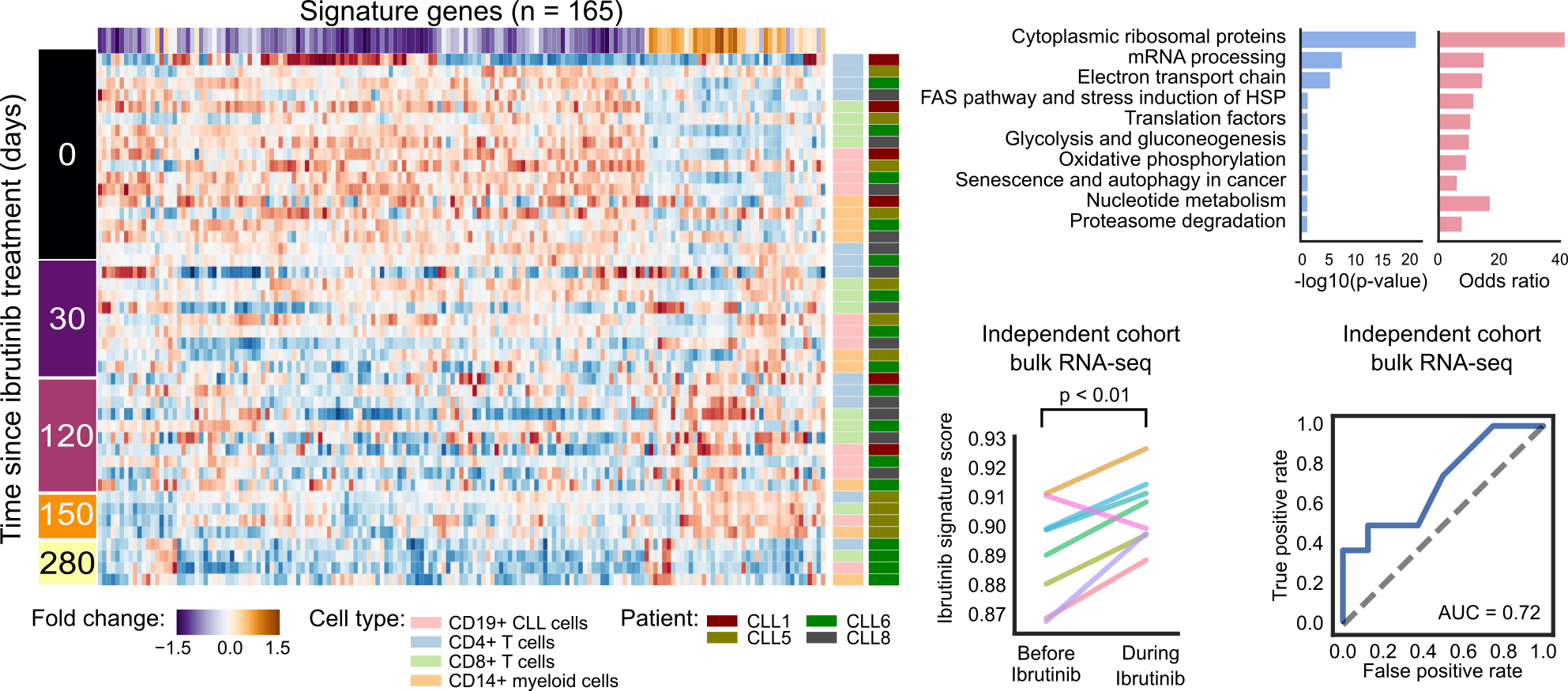
Ibrutinib treatment induces a quiescent-like state in CLL cells that is shared with other immune cells
Data
This section provides access to raw data and analysis results underlying the presented temporal analysis of ibrutinib-treated CLL.
| Name | Description and link |
|---|---|
| Raw and processed ATAC-seq and scRNA-seq data |
GEO SuperSeries accession: GSE111015
GEO Series on ATAC-seq data: GSE111013 GEO Series on scRNA-seq data: GSE111014 |
| Temporal immunophenotyping of CLL patients during ibrutinib therapy |
Immune cell type composition: download here Expression of surface receptor markers: download here |
| Temporal chromatin changes in sorted immune cell types of CLL patients during ibrutinib therapy | download here |
| Temporal expression changes in single cells of peripheral blood of CLL patients during ibrutinib therapy | download here |
Citation
If you use these data in your research, please cite:
André F. Rendeiro1*, Thomas Krausgruber1*, Nikolaus Fortelny1, Fangwen Zhao1, Thomas Penz1, Matthias Farlik1, Linda C. Schuster1, Amelie Kuchler1, Szabolcs Tasnády2, Marienn Réti2, Mátrai Zoltán2, Donat Alpar1†, Csaba Bödör3†, Christian Schmidl1,6†, Christoph Bock1,4,6† (2018).
Chromatin mapping and single-cell immune profiling defines the temporal dynamics of ibrutinib drug response in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
* These authors contributed equally to this work
† Co-last author / These authors jointly directed this work